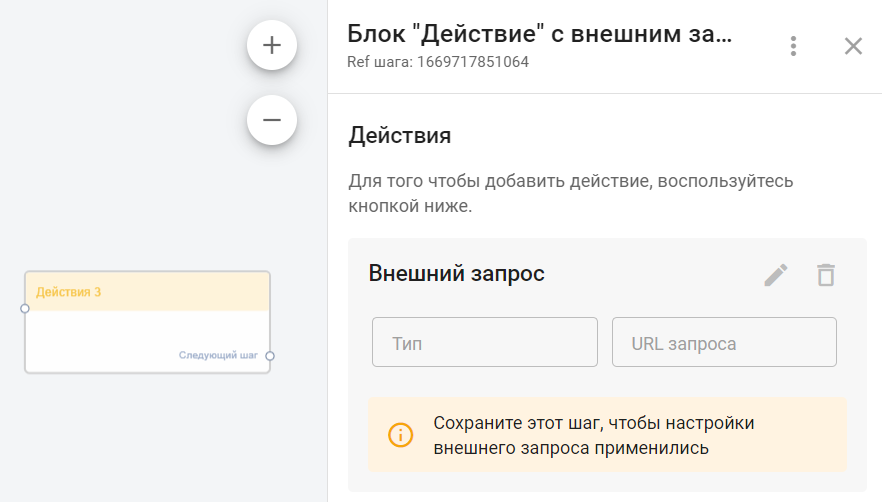
"External Request" can be found in the bot builder in the "Action" block in the drop-down list of actions.
Examples of scenarios for using "External Request" in bots
1. "Subscriber chooses which Star Wars character he is": link .
- Sending request.
- Testing the request.
- Describing a simple JSON Path and writing data from the response to a custom field.
- Using the received data in the bot.
2. Integration with Google Sheets to read data from a table: link .
- Setting up and preparing a Google account for integration.
- Sending and testing the request.
- Describing a more complex JSON Path and writing data from the response to a custom field.
- Using the received data in the bot.
3. Sending SMS via the Aero SMS : link to video .
4. Random Number Generator: link .
5. Sending notifications to the agent in Telegram : link .
6. Issuance of certificates through the GramotaDel : link to video .
General description
The External Request action allows you to:
- Send requests to external services via their API. Available request types:
- GET
- POST
- PUT
- PATCH
- DELETE
- Write data received from an external service in response to a sent request to custom subscriber fields.
- As a test, send a request and receive a response inside a modal window.
- If macros are used to send a request, then during testing, test data will be substituted instead of them, the values of which can be changed before testing.
All settings for the "External Request" are performed in a separate pop-up (modal) window that opens during editing.
The setup and purpose of all the elements of the "External Request" are described below.
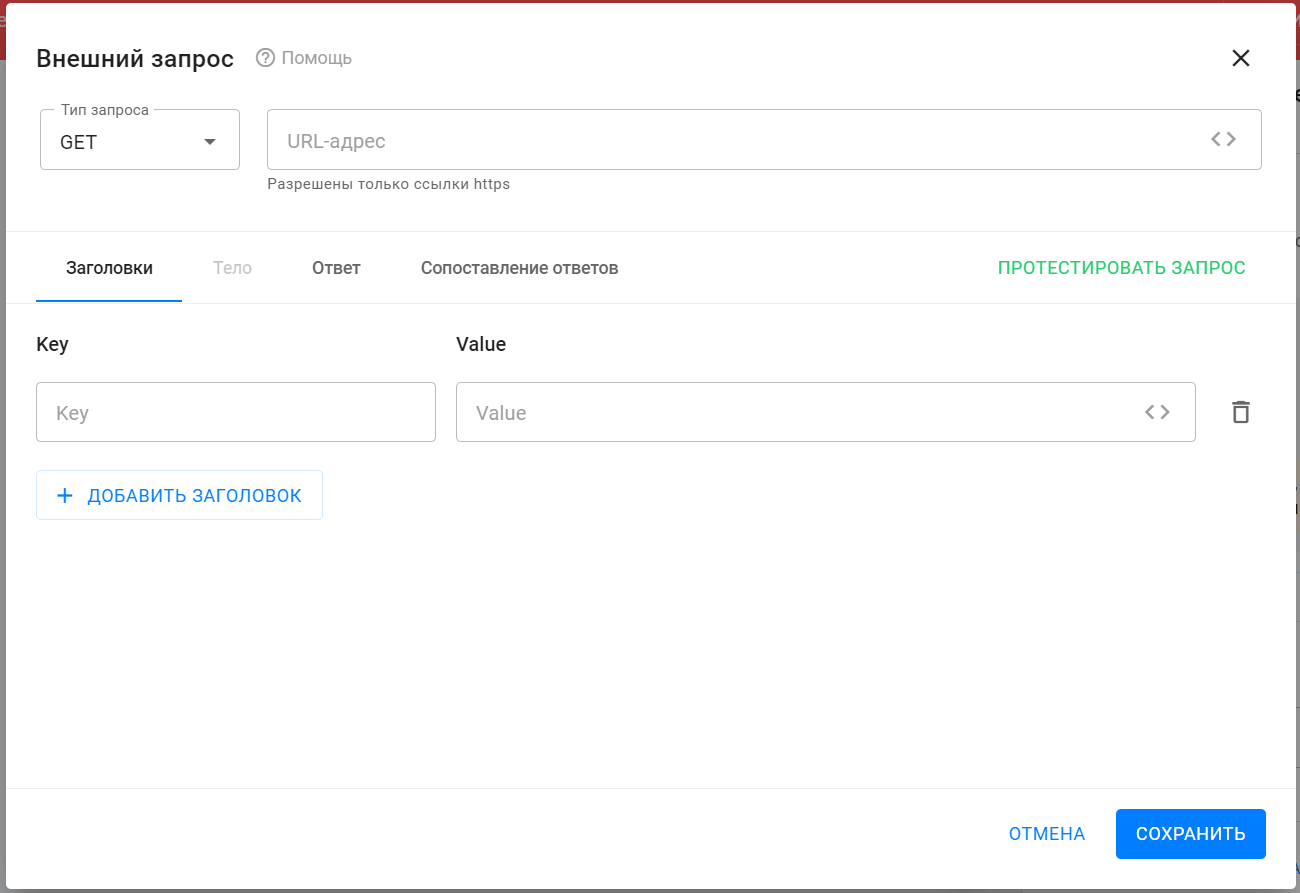
Request type and URL
In the "Request Type" drop-down list, select the type of request to be sent. You need to look for it in the description of the API service with which you are setting up interaction.
In the "URL" field, specify the address to which the request will be sent. You should also look for it in the service API description.
When entering a URL, you can use standard macros (all macros that are in your account). To add macros to a link, you need to:
- after the link itself put the sign "?»;
- when listing parameters, connect macros with the " sign&».
Example: link.ru?utm_content=1&{%pole%}.
Headings Section
This section specifies the headers for the request being sent.
You can:
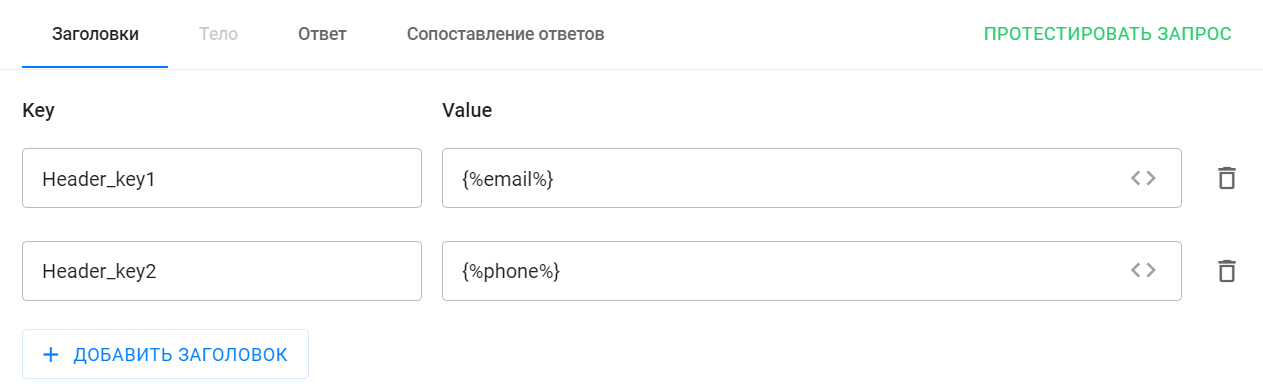
- add/remove headings;
- use standard macros in the field with the value "title". When using macros, the title value will be different for each subscriber.
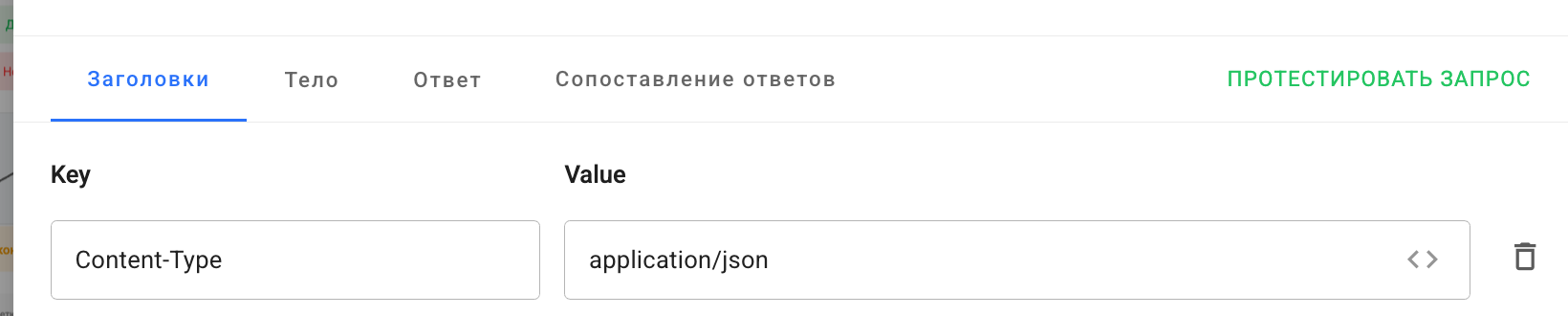
Important! For correct operation of data comparison, it is necessary the Content-Type header both in the request and in the service response.
Valid values: application/json and text/html
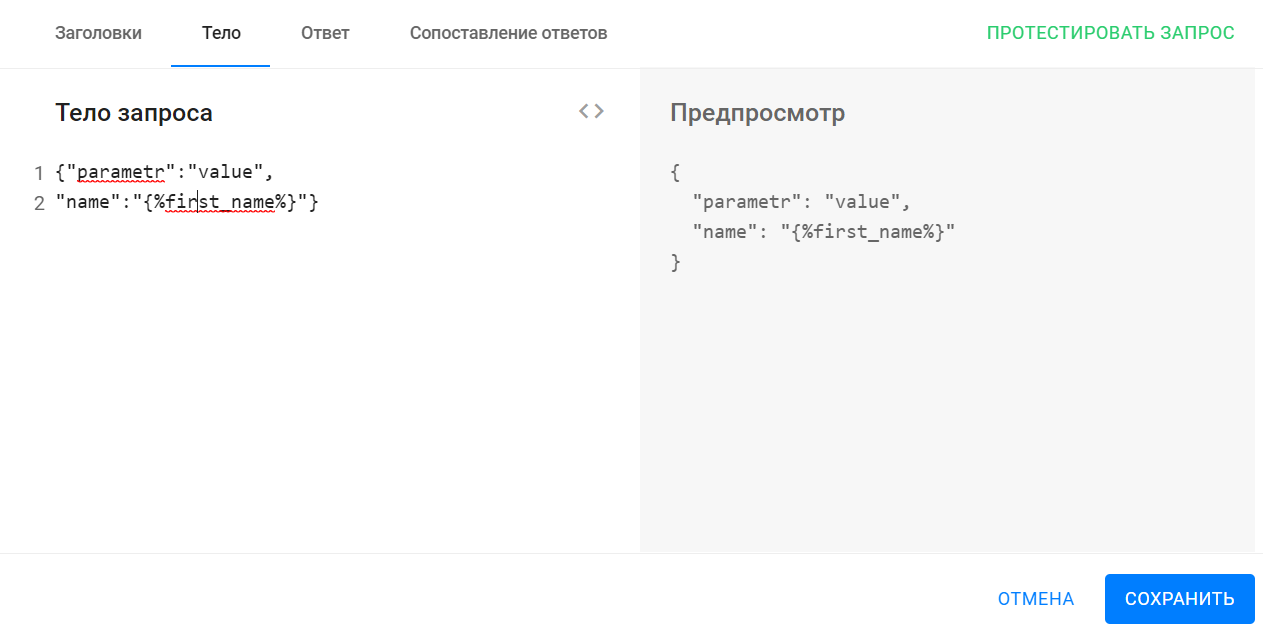
Section "Body"
This section describes the body of the request. For this section, you need to take the code from the settings of the third-party service.
The body must be described in JSON format.
When filling out the request body, the use of standard macros is allowed.
In the right part of the "Preview" automatic validation and formatting of the entered body is performed.
IMPORTANT! This section is not available for GET type requests.
Answer Section
This section displays the response that will come from the external service when the request test is started.
To start testing your request, click Submit Request or Test Request .
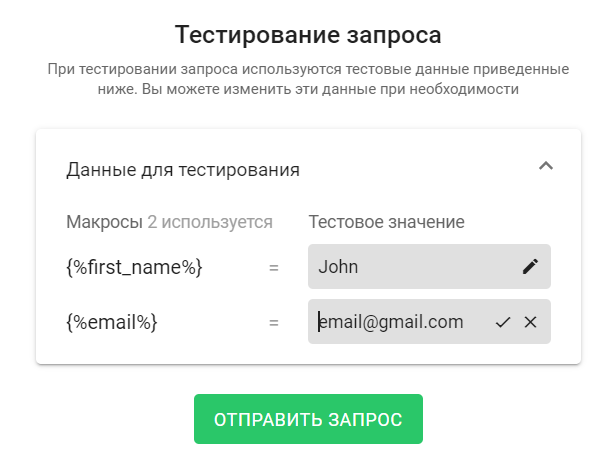
If you use macros in the headers, body, or URL, the macros will be replaced with test values during testing. You can change the test values by opening the "Test data" drop-down list and changing the value in the "Test value" field for the desired macro.
After you successfully send a test request, the received response will be displayed on the right side of the tab. You can see the response headers and the response body itself.
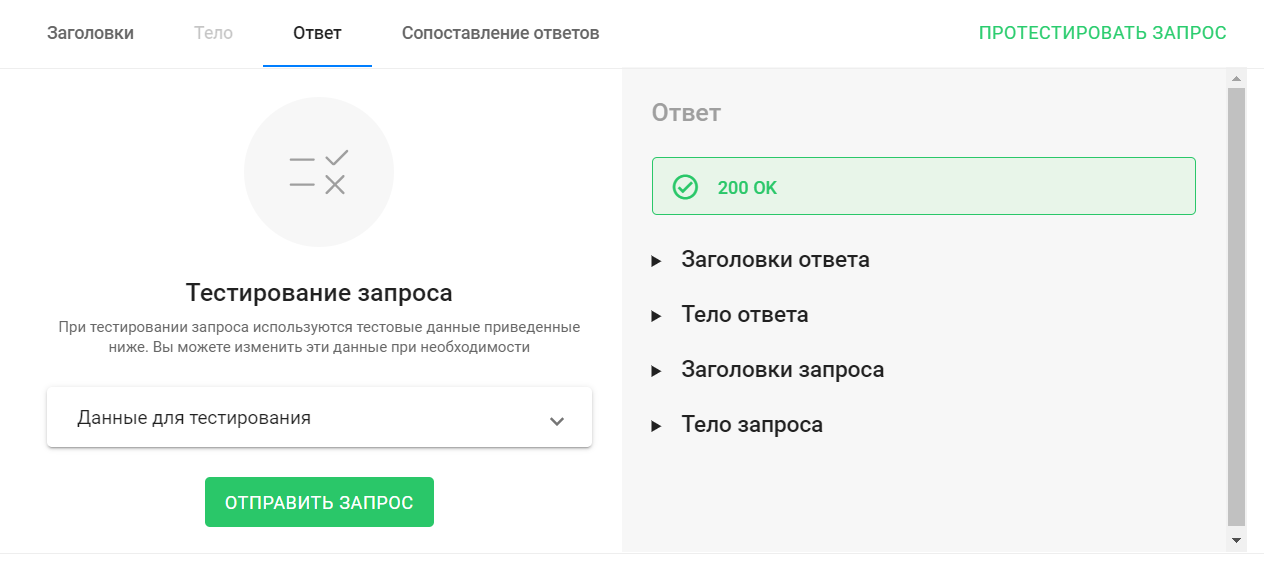
The values received in the response body can be saved to subscriber custom fields using the Response Mapping tab.
Section "Comparison of answers"
In this section, you can configure response mapping so that the data received in response to the request is written to the specified subscriber custom fields.
The data and its structure can be viewed when the request testing starts, on the Response tab in the Response Body section:
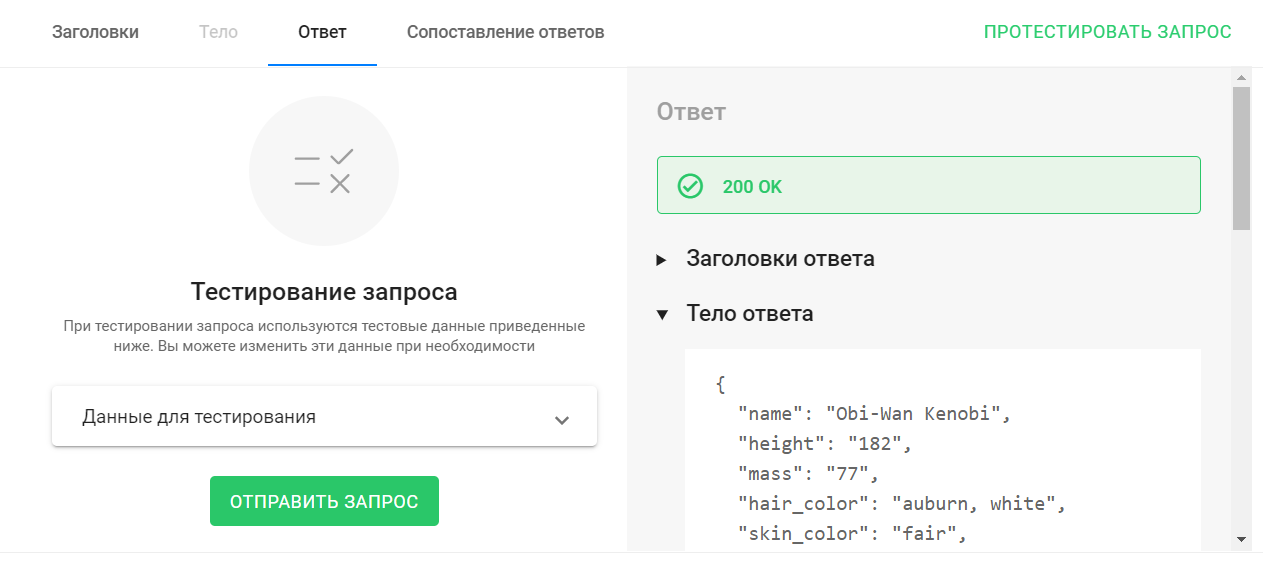
This tutorial describes a scenario with testing a request, setting up matching, and then using the data in a bot.
To set up the mapping you need to:
- add a matching rule by clicking on the + add matching ;
- specify JSON Path — the path in the response body from which the received value should be retrieved. Detailed instructions on how to write JSON Path;
- Specify a custom field in which the value received in the response will be saved.
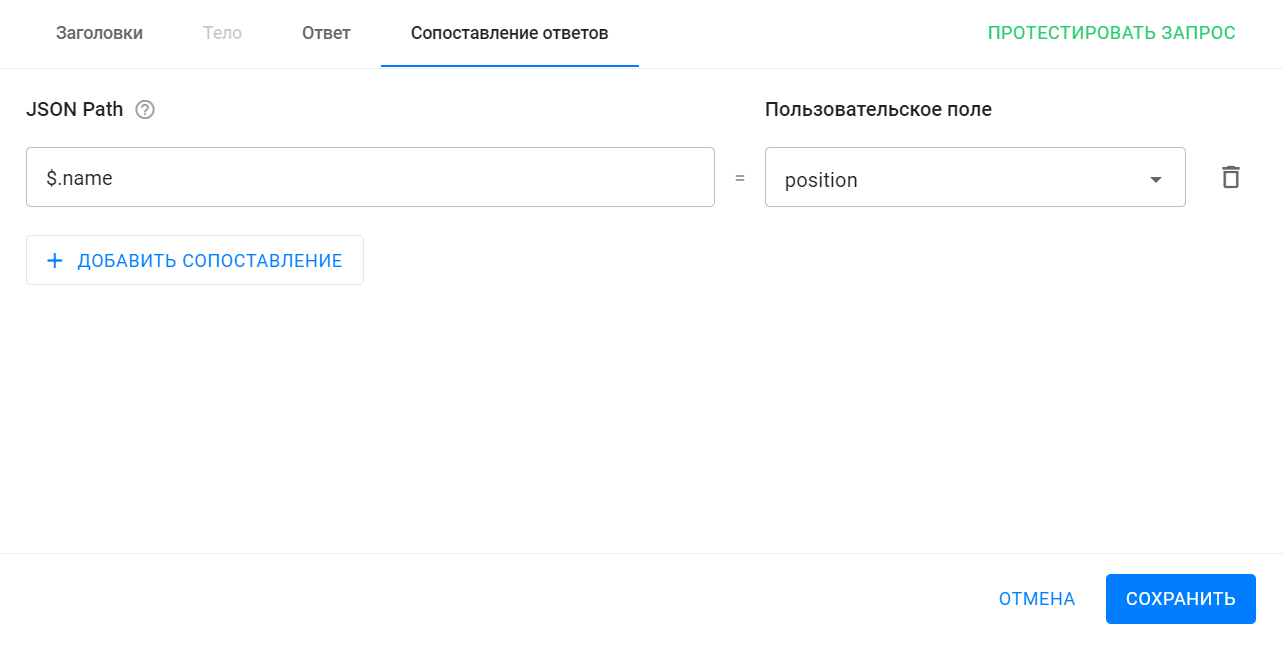
IMPORTANT! After setting up and testing your query, be sure to click Save .
IMPORTANT! To prevent the external query settings from being reset, be sure to save the Action step in which you added the external query.
Frequently asked questions
Where can I get Key for Headers?
It depends on the service and the method with which the integration is configured via an external request. The description of the settings of the third-party service will contain a list of data, where and what keys to insert.
Examples of using external query
Automatic issuance of personalized certificates.
Sending SMS messages to subscribers.
Notifications in the telegram channel.
The External Request action allows you to send or request information from external services, and then receive a response from them and write it to the subscribers' custom fields.
Below we will consider the simplest scenario of how to use the "External Request" action. This scenario is far from real, but it shows all the stages of setting up and the functionality of the "External Request".
Description of the scenario and its settings
In this example, we use the swapi.dev . The service stores information about the Star Wars film series: film titles, character names and their characteristics, descriptions of vehicles, planets, races, and so on.
In other words, this service is a Wikipedia on the Star Wars universe.
Main stages of the script
- The subscriber gets into the bot.
- The bot sends a request to the swapi.dev service with the subscriber ID.
- The service returns a description of the character whose ID is the same as the subscriber's.
- The bot writes the character's name into the custom field and displays this value to the subscriber.
Setting up the bot
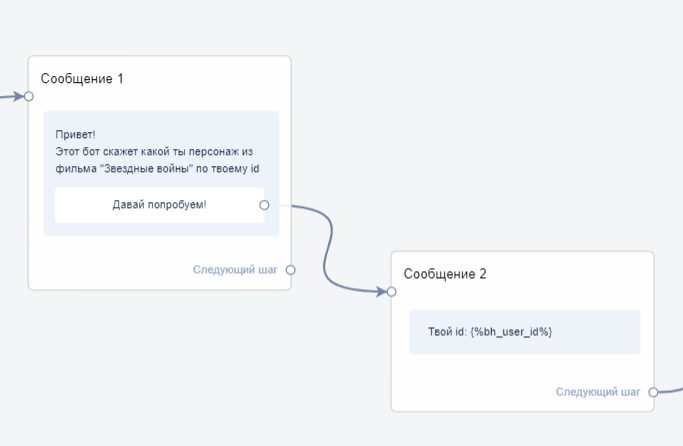
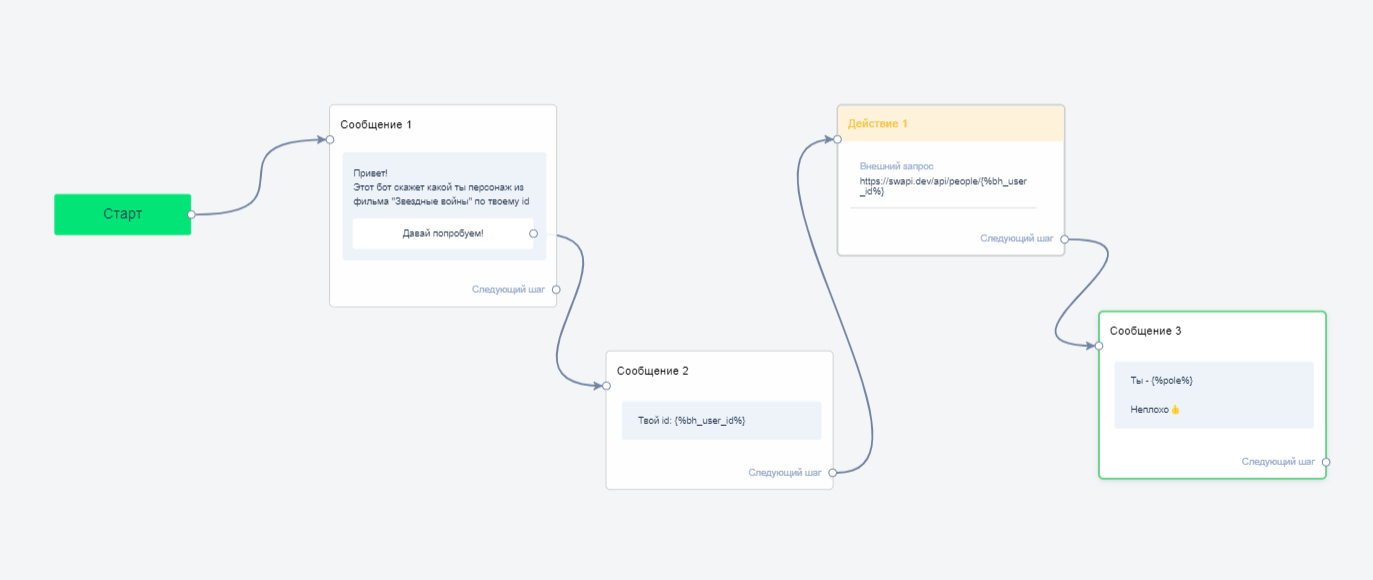
Build a simple bot chain:
- Add a block "Message 1".
- Write a welcome text.
- Add a button to move to the next step.
- Add a block "Message 2".
- Display the user's ID.
- Using this ID, the external service will find the character in its database.
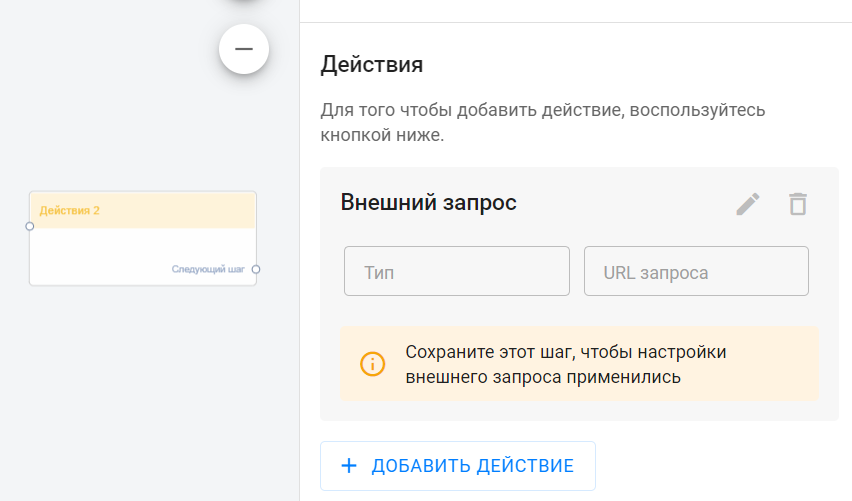
- Add an Action 1 block.
- In this block, select the “External request” action (we will discuss the external request settings below).
- Add a block "Message 3".
- Output a custom field in which you will write the character name received from an external service.
- Connect all the blocks and you will get a small bot like this:
Setting up an "External Request"
- When you add the "External Query" action in the "Action 1" block, click on the "pencil" to open the "External Query" editing window. Then you need to configure everything in the window that opens.
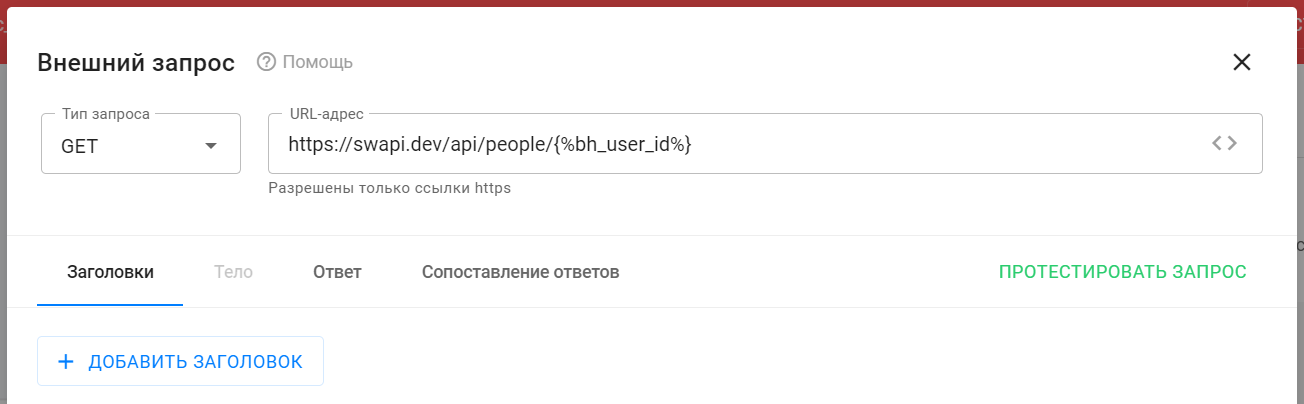
- Enter the request URL.
- In the description of the swapi.dev service, select the method that will return the character's characteristics: https://swapi.dev/api/people/ 1 /
- Copy and paste the address into the URL field.
- In this address, "1" is the character ID. Instead of this value, insert a macro that will automatically substitute the subscriber's internal ID. To do this, click on the <> in the "URL address" field and select the desired macro.
- Final link: https://swapi.dev/api/people/{%bh_user_id%}
- Select the request type.
- The type of this request is GET. This information should be on the external service's website with a description of its API. Select GET in the "Request type" drop-down list.
- There are no headers or body to fill in with this method, so move on to testing the request.
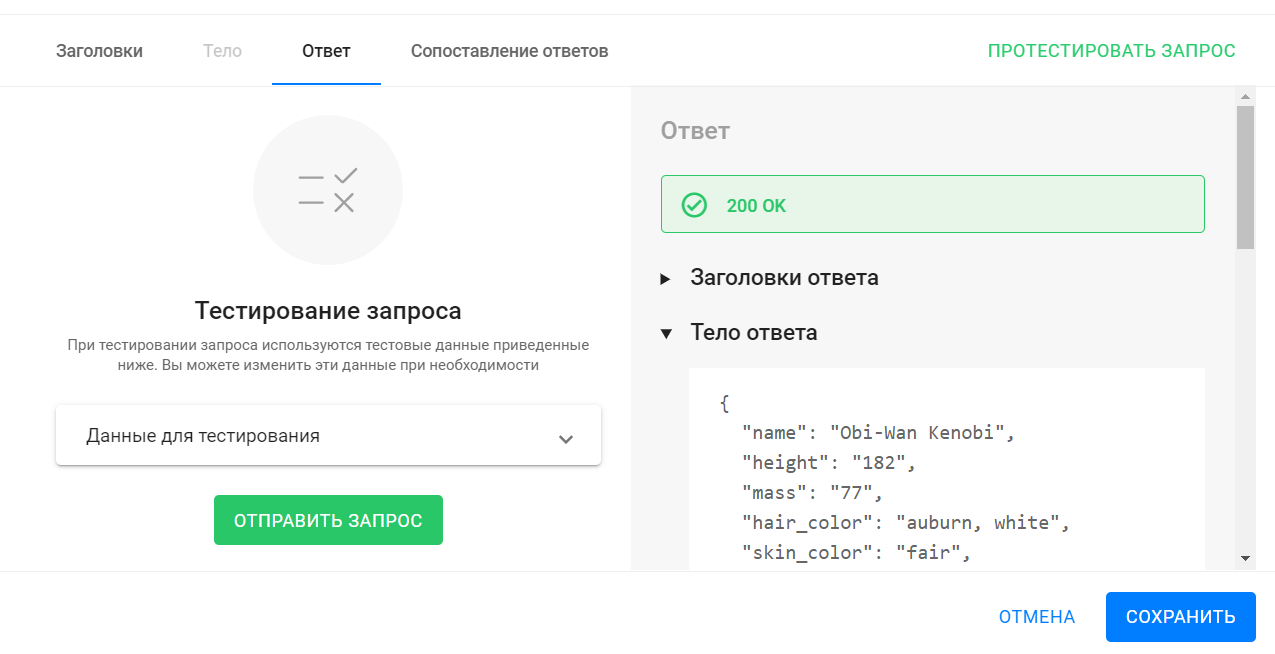
- To test the request and make sure everything works correctly and the service returns the correct response, go to the Response tab or click the Test Request .
- In the opened tab you see test data for the used macros. The default value is 10. You can change it if necessary.
- To start testing, click the Send Request .
- The response is “200 OK”, which means the external service received your request and successfully returned a response.
- On the right side of the window, in the "Response Body" section, you can see what you received in response to your request.
- You need the value of the "name" field. It is the value of this field that you will automatically write to the subscriber's custom field.
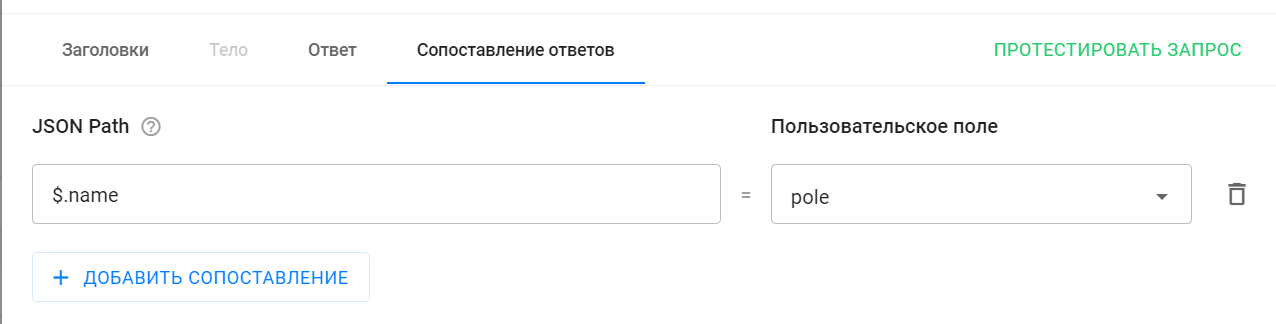
- Set up response matching.
- Response mapping allows you to set up logic that will take the value of the required field from the received response body and write it to the specified subscriber custom field.
- To do this, you need to specify the path by which you want to find the required field in the response body ( read more here ), and the user field itself in which you want to save the value.
- Add a mapping and fill in the fields that appear.
- The JSON Path value "$.name" will return the value of the "name" field from the body of the response received. In the example from testing, the value was "Obi-Wan Kenobi".
- This completes the setup of the External Request.
- Be sure to save its settings by clicking on the Save .
- Be sure to save the settings of the open step "Action 1" by clicking on the Save and Close .
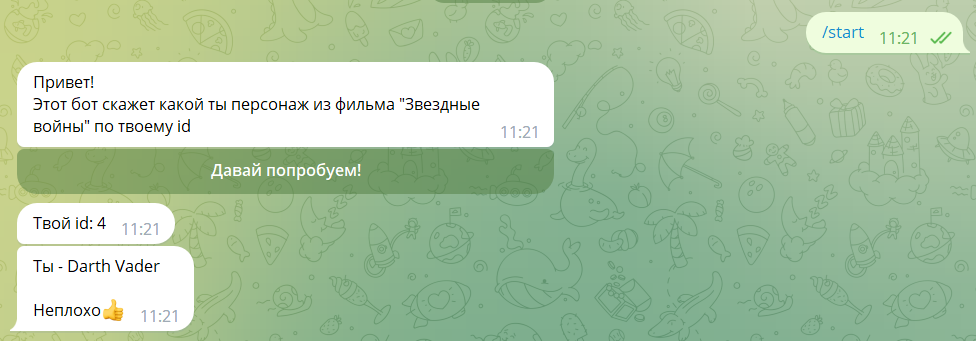
Testing the bot with an external request
- Start testing the bot.
- As a result, you will receive a chain of messages like this:
I am Darth Vader, who are you? :)
A general description of the external request action can be found here: link .
If you have not found the answer to your question, ask us in the chat inside your account or write to BotHelpSupportBot or to hello@bothelp.io
Get 14 days of full functionality of the platform for creating mailings, autofunnels and chatbots BotHelp.